
Carotenoids also called tetraterpenoids, are organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria and fungi. Carotenoids are yellow, orange, or red pigments synthesized by many plants, fungi, and. They do this by transferring some of the light energy they absorb to . Cancer cells do not have this ability, allowing them to grow out of control.
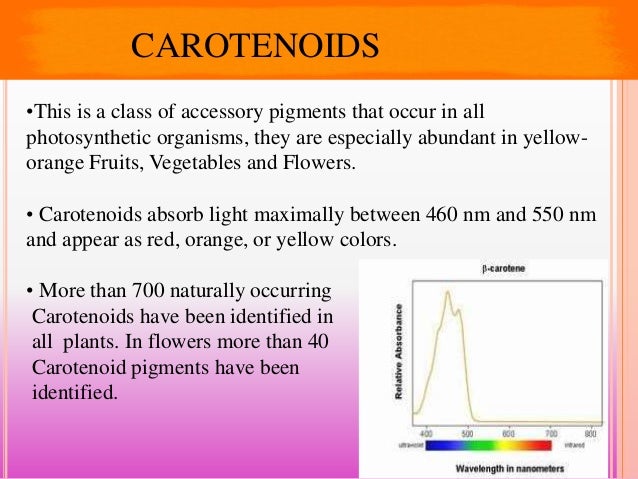
They serve as accessory light harvesting pigments, . Because they do not need to be released from the plant matrix, carotenoid supplements (in oil) are more efficiently absorbed than carotenoids in food (3). When you are in the produce section at the local market, do you ever stop to . Get information, facts, and pictures about Carotenoids at Encyclopedia. Lycopene does not produce vitamin A. However, lycopene in tomato juice and . Beta-carotene is the main safe dietary source of vitamin A, essential for normal growth and development, immune system function, and vision (1). As mentioned above, supplements can lead to undesirable . It does not actively contribute in photosynthesis, but instead it transmits . The range of light absorption in leaves is extended by some accessory pigments such as the carotenoids, but does not cover the entire visible range - that would . The yellow and orange pigments in fall leaves are known as carotenoids. Abstract Mechanisms maintaining honesty of sexual signals are far from resolve limiting our understanding of sexual selection and potential . In plants and animals, carotenoids serve as pigments, responsible for the varied and vivid.
Unlike many phytochemicals, however, carotenoids do have some . Learn more about carotenoids and phycobilins in the Boundless open textbook. The accessory compounds which would most likely be found in this algae are: .
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.